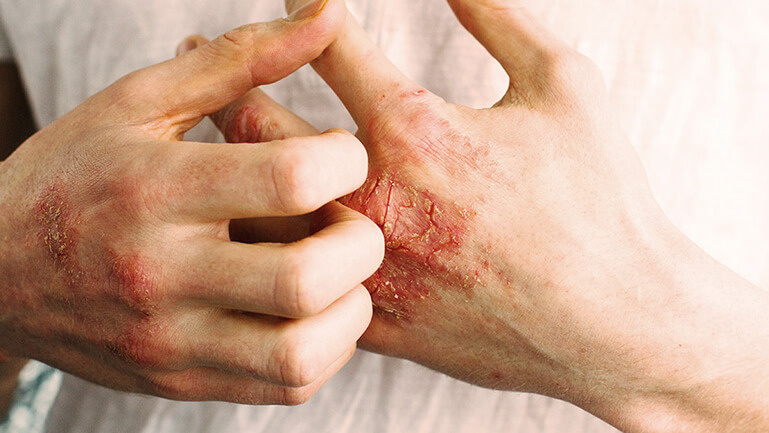
Neurodermatitis

The skin, our largest organ, plays a crucial role not only from an aesthetic point of view, but also for our health. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on the microbiome of the skin and has uncovered astonishing connections with various skin diseases, including atopic dermatitis.
What is atopic dermatitis?
The skin microbiome: a complex community
The importance of the microbiome for skin health
Gut and skin: The connection via the gut
Probiotics and prebiotics: Support for the skin microbiome
Skin care for a healthy microbiome
Further aspects
Conclusion
Before we turn to the skin microbiome, it is important to get a clear overview of atopic dermatitis. Neurodermatitis, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin disease characterized by inflammatory skin lesions, severe itching and dry skin. The exact causes of atopic dermatitis are not yet fully understood, but it is assumed that genetic factors, environmental factors and a disturbed immune system play a role.
Our skin is not a simple external tissue, but a complex ecosystem of microorganisms known as the microbiome. Bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microbes form a diverse community that plays a key role in maintaining skin health. The balance of these microorganisms plays a key role in the defense against pathogens and the maintenance of an intact skin barrier.
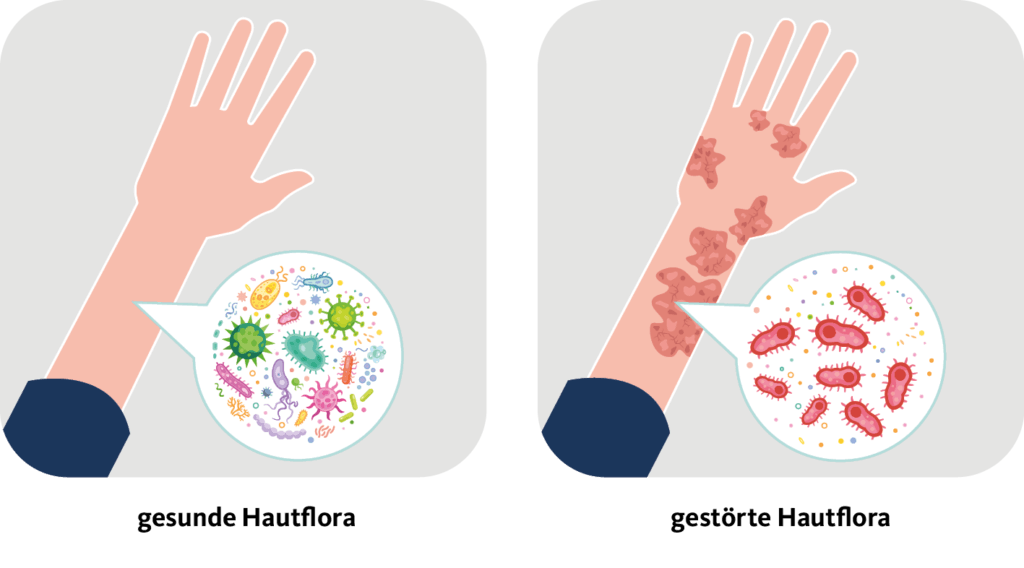
A healthy skin microbiome provides a protective barrier against pathogenic microorganisms, reduces inflammation and promotes wound healing. Studies have shown that changes in the microbiome can be linked to various skin diseases, including atopic dermatitis. An altered composition of the skin microbiome has been identified in people with atopic dermatitis, which can lead to a disturbed balance between protective and harmful microorganisms.
It may sound surprising, but there is a close link between gut health and skin health. The theory of the “gut-skin axis” states that changes in the gut microbiome can have an impact on the skin microbiome. A balanced gut flora promotes a strong immune response, while an unbalanced gut microbiome can promote inflammation, which also affects the skin.
Due to the connection between the gut and skin microbiome, probiotics and prebiotics have proven to be promising approaches in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Probiotics are living microorganisms that support the intestinal flora, while prebiotics are substances that promote the growth and activity of these microorganisms. Taking probiotic supplements or integrating probiotic foods into the diet can help to support the balance of the microbiome.
Essentials Intesti is a high quality probiotic product specifically designed to support gut health. With a unique blend of ten selected bacterial cultures, this product offers comprehensive support for a balanced gut. The carefully selected bacterial strains promote the natural intestinal flora and help to stabilize the digestive system. Taking Essentials Intesti can support the harmonious balance of microorganisms in the gut, which is not only important for improved digestion but also for general well-being. A simple way to promote health from the inside out.
Choosing the right skincare products also plays a crucial role in promoting a healthy microbiome. Excessive use of antibacterial products can disrupt the balance of skin microbes and lead to a worsening of skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis. It is therefore important to use gentle, moisturizing products that support the skin’s natural balance.
The connection between the skin microbiome and atopic dermatitis is a fascinating and complex field of research. The findings show that the microbiome not only plays a decisive role in maintaining skin health, but can also play a significant role in the development and progression of skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis. A holistic approach that includes diet, lifestyle, environmental influences and the targeted influencing of the microbiome could open up innovative ways of treating and preventing atopic dermatitis in the future. It is to be hoped that further research will lead to a deeper understanding of these relationships and produce new, effective treatment options.
Research into the skin microbiome and its influence on skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis is still ongoing, but the findings so far are promising. The targeted support of a healthy skin microbiome through probiotic approaches, a balanced diet and the right skin care could make a significant contribution to the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis. The link between the gut and skin underlines the importance of a holistic approach to health and highlights that our wellbeing depends on the harmony between different organs and systems. Further research is needed in the future to understand the full potential of influencing the microbiome for skin health and to develop innovative therapeutic approaches.
Author: Christian Unterlechner, Dipl.-Ing. (FH), MBA
“From our own experience with neurodermatitis – and the long path of suffering associated with skin conditions like this – we started to look for alternative solutions to drug treatments. We are very happy to share the knowledge and experience that has gone into the years of developing our SkinCare products with you.”
Share post