Dermatologists are increasingly having to test for atopic dermatitis.
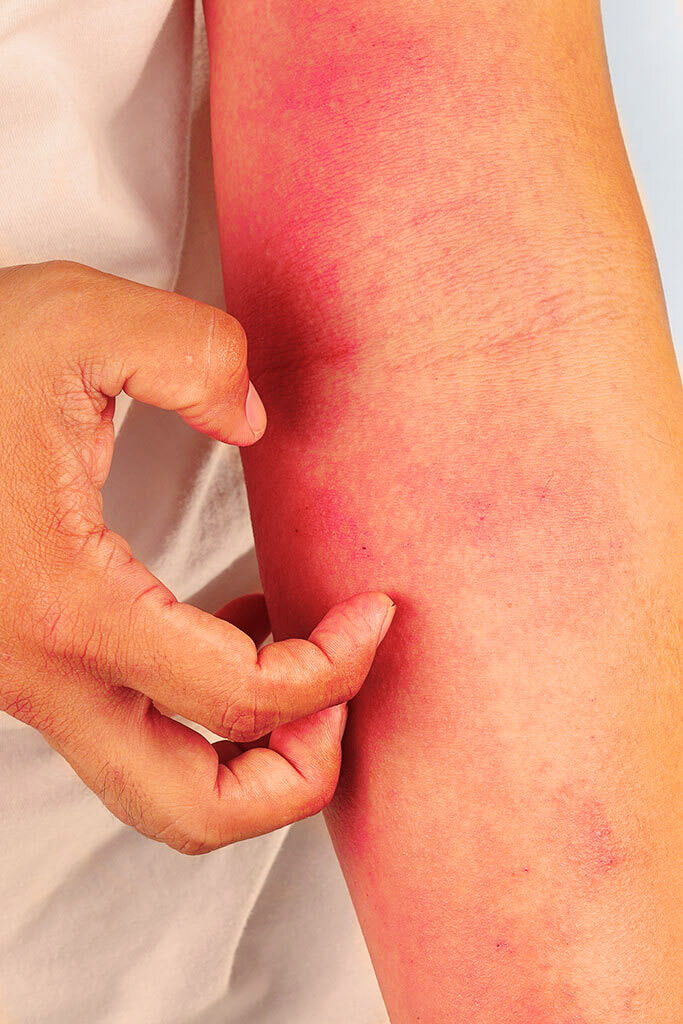
This chronic inflammatory skin disease, also known as atopic eczema, is characterized by itchy eczema on sensitive, very dry skin that occurs in episodes.
As different as we humans are, the triggers of acute flare-ups can be just as different.
Symptom-free phases are quite possible if you manage to avoid things that trigger a flare-up.
The suffering of neurodermatitis sufferers and their family members is immense, but once neurodermatitis has been identified, special therapies can be used to alleviate acute neurodermatitis symptoms and prolong the period without symptoms.
We explain what triggers the disease and how you can restore balance to your reddened skin.
The healthy balance of our skin depends heavily on the many different microorganisms that normally live on the surface and in the niches of our skin being able to colonize in sufficient quantities and in the right places. This protects the skin against external attacks.
If the bacterial cocktail of our skin, the so-called skin microbiome, gets out of balance, danger is imminent. Inflamed skin irritates and distresses the patient.
This is because otherwise harmless germs that have been living a shadowy existence until now can suddenly multiply uncontrollably and develop into pathogens that promote atopic dermatitis.
Due to the impaired skin barrier, neurodermatitis sufferers are more likely to suffer from viral and bacterial infections than healthy people.
The causes of the overreaction of the immune system are still not fully understood. However, genetics is probably responsible for the predisposition to atopic dermatitis.
An international study by the Helmhotz Center in Munich has succeeded in identifying several DNA segments and thus genes that increase the risk of the disease.1
One of these gene mutations leads to the protein filaggrin being produced only to a limited extent or not at all. This protein is an important building block of the epidermis.
If filaggrin is missing, typical symptoms of neurodermatitis such as abnormal dryness and weakened skin barrier function are the result.
Allergens from the environment, as well as bacteria and viruses, can now penetrate more easily and thus promote the development of diseases such as atopic eczema.
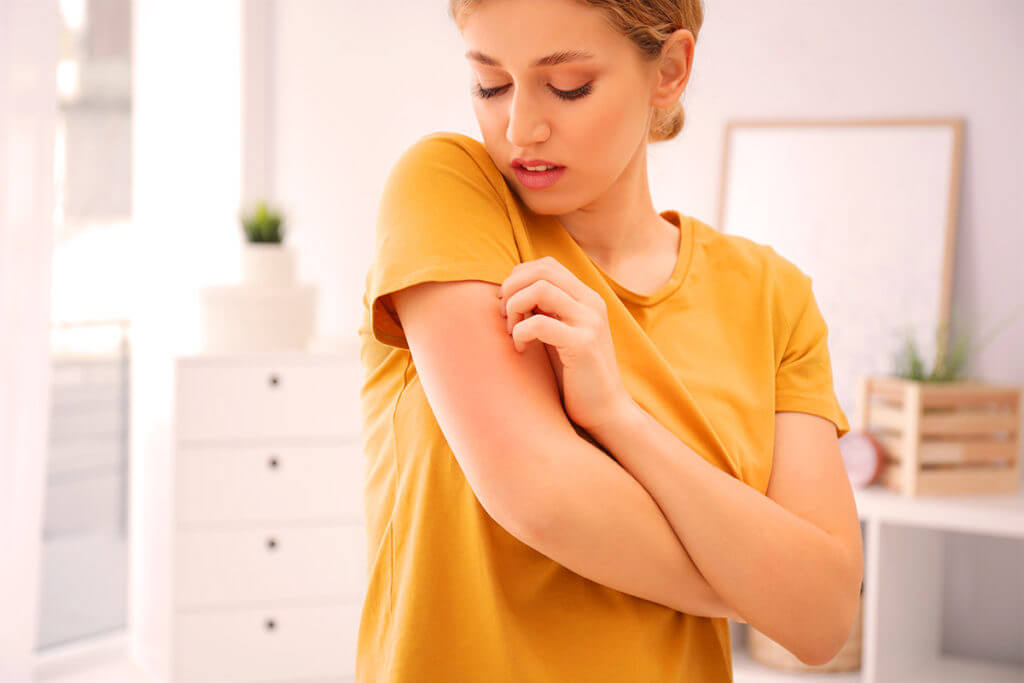

The wrong soap or bathing for too long, scratchy clothing, the wrong diet for atopic dermatitis or “just” stress – there are numerous triggers that can irritate the sensitive skin of atopic dermatitis and lead to an acute flare-up.
However, which triggers are significant for the course of the disease varies greatly from person to person.
The following lists can be responsible for an atopic dermatitis flare-up:
Neurodermatitis cannot be cured according to current knowledge. However, the symptoms can be alleviated by regenerating and stabilizing the disturbed skin microbiome.
This includes consistent, targeted care. In severe cases of atopic dermatitis, a visit to the doctor is recommended in any case.
The penetration of germs and irritants is made more difficult and the extreme dryness of the skin is alleviated.
Agonizing itching, inflammation and similar symptoms can be reduced with the use of phages.
The aim is to eliminate only the problematic bacteria on the skin without damaging the skin microbiome at the same time. Only bacteriophages work so precisely.
These are viruses that usually only infect and kill one type of bacteria, but are harmless to humans.

In addition to foods such as eggs, milk, fish or nuts, other allergens such as house dust mites or pollen can also trigger atopic dermatitis.
Sugar and foods containing gluten do not play a role in atopic dermatitis. On the other hand, you should be careful with eggs, cow’s milk, peanuts and fish, as these foods are often associated with atopic dermatitis.
A gamma-linolenic acid deficiency can occur in neurodermatitis, as the absorption and conversion does not take place to the required extent in neurodermatitis patients due to an enzyme defect.
The psyche cannot be the cause of neurodermatitis. However, the psyche plays a major role in the course of the disease and can suffer greatly. A poor mental state can also worsen the healing process.
Black tea can soothe inflammation of the skin. To do this, a cloth soaked in tea is placed on the affected areas up to 5 times throughout the day for 20 minutes at a time. Afterwards you should cream the skin with e.g.
SkinCare Sensitive
.
Also
SkinCare Protect
helps to reduce inflammation and kill harmful bacteria.
Author: Christian Unterlechner, Dipl.-Ing. (FH), MBA
“From our own experience with neurodermatitis – and the long path of suffering associated with skin conditions like this – we started to look for alternative solutions to drug treatments. We are very happy to share the knowledge and experience that has gone into the years of developing our SkinCare products with you.”
Share post