Reduziere Neurodermitis
mit Sanubiom SkinCare Protect mit Phage Technology
Neurodermatitis
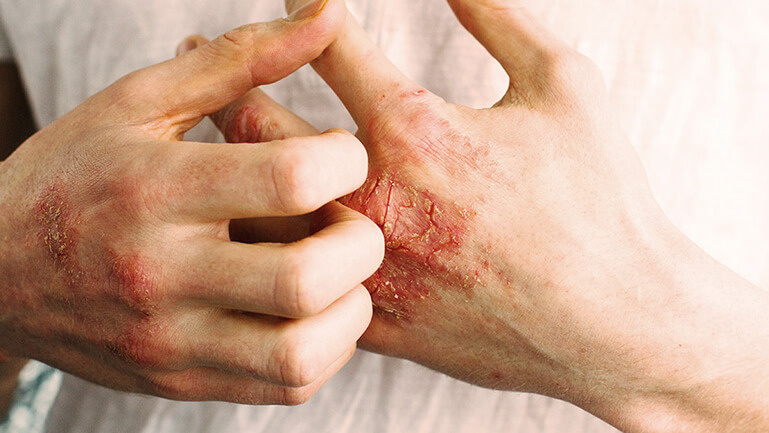
Itchy, red, flaky skin? These can be signs of the insidious skin disease atopic dermatitis. Neurodermatitis (also known as “atopic dermatitis”) is one of the most common skin diseases of our time. It is a chronic inflammatory skin disease and occurs in episodes. It can affect many parts of the body, including the scalp, face and hands, but also the elbows and knees and many other areas.
Eczema and inflammatory skin changes with agonizing itching are typical of neurodermatitis, which occur repeatedly in episodes. A period without symptoms can be followed by a phase of extreme discomfort. These flare-ups are usually triggered by certain factors such as food or weather conditions.
The severity of the symptoms can also vary greatly, with some patients experiencing quite mild courses, while others suffer severe outbreaks of atopic dermatitis.
Neurodermatitis can have a variety of manifestations. Typical symptoms of this are
Babies and toddlers suffer most frequently from atopic dermatitis. The first symptoms at this age appear in the form of cradle cap, red, scaly skin and itching. However, cradle cap alone, without other symptoms, is not a sign of neurodermatitis. At this young age, eczema usually appears on the outside of the arms and legs, but in some cases, weeping eczema can also develop around the mouth. In the 1st year of life, children can develop so-called flexural eczema, reddened, scaly patches of skin in the folds, which are covered with crusts.
The affected areas include the back of the knees, elbows and wrists. However, the skin is dry and can hardly store any moisture. If the little patients scratch themselves, the open skin areas can become infected with bacteria, viruses or herpes. In particular, babies with close relatives who suffer from atopic dermatitis are more likely to also develop atopic diseases. This also includes hay fever, food allergies and allergic asthma.
Sometimes the skin condition can disappear during adolescence and disappear during puberty, but it can also persist into adulthood.
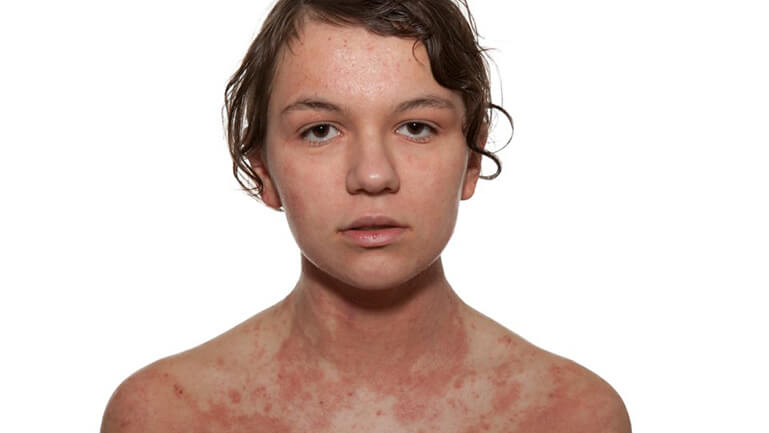
As many skin diseases cause the same symptoms as neurodermatitis, the diagnosis should only be made by a qualified dermatologist.
Atopic eczema is an indication:
The typical signs of atopic eczema are
Allergic reactions can trigger or aggravate neurodermatitis. Patients with atopic eczema have elevated immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, which plays an important role in allergic reactions. However, it is also possible to have elevated immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels in the blood due to a predisposition without suffering from atopic dermatitis.
Allergy tests are useful to find out what people react to. There are two different tests, the detection of specific antibodies in the blood against inhalation and food antigens and the prick test. In this test, the doctor scratches small amounts of allergen into the skin and assesses the patient’s skin reaction after 15 minutes. If a positive result is available, it can only be concluded that the patient is sensitive to the allergen, but not that this allergen is also responsible for atopic dermatitis.
The skin of patients with neurodermatitis, but also inflamed skin in general, is often heavily colonized with Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. With their metabolic products, these bacteria contribute to the repeated re-inflammation of the skin.
SkinCare Protect, which uses Phage Technology to specifically attack and kill bad bacteria, is suitable as a safe treatment. Once the harmful bacteria have been removed from the skin, the skin can begin to regenerate.
Locally applied antibacterial substances (antiseptics) can have an improved effect, especially on inflamed skin. However, these are not suitable for permanent use.
Antibiotic ointments and creams can develop resistance with long-term use and should therefore only be used under medical supervision. Contact allergies can also occur.
Author: Christian Unterlechner, Dipl.-Ing. (FH), MBA
“From our own experience with neurodermatitis – and the long path of suffering associated with skin conditions like this – we started to look for alternative solutions to drug treatments. We are very happy to share the knowledge and experience that has gone into the years of developing our SkinCare products with you.”
Share post